Strategy Design Pattern
The Strategy Design Pattern is a behavioral design pattern that allows us to define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one, and make them interchangeable. This pattern enables an object to choose from multiple algorithms or behaviors at runtime, rather than being hardcoded to use a single one.
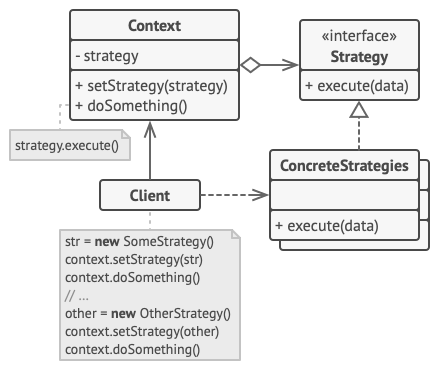
Key Components:
- Strategy Interface: This defines a common interface for all supported algorithms.
- Concrete Strategies: These are classes that implement the Strategy interface, each providing a different algorithm.
- Context: This is the class that uses a Strategy. It maintains a reference to a Strategy object and can switch between different strategies dynamically.
Benefits:
- Flexibility: We can change the behavior of an object at runtime.
- Maintainability: Adding new algorithms or modifying existing ones is easier since they are encapsulated in separate classes.
- Adherence to the Open/Closed Principle: Classes are open for extension but closed for modification.
Example in Java:
Here’s a simple example to illustrate the Strategy Design Pattern:
// Strategy Interface
public interface PaymentStrategy {
void pay(int amount);
}
// Concrete Strategy for Credit Card Payment
public class CreditCardPayment implements PaymentStrategy {
private String cardNumber;
public CreditCardPayment(String cardNumber) {
this.cardNumber = cardNumber;
}
@Override
public void pay(int amount) {
System.out.println("Paid " + amount + " using Credit Card.");
}
}
// Concrete Strategy for PayPal Payment
public class PayPalPayment implements PaymentStrategy {
private String email;
public PayPalPayment(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public void pay(int amount) {
System.out.println("Paid " + amount + " using PayPal.");
}
}
// Context Class
public class ShoppingCart {
private PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy;
public void setPaymentStrategy(PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy) {
this.paymentStrategy = paymentStrategy;
}
public void checkout(int amount) {
paymentStrategy.pay(amount);
}
}
// Usage
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShoppingCart cart = new ShoppingCart();
// Pay using Credit Card
cart.setPaymentStrategy(new CreditCardPayment("1234-5678-9876-5432"));
cart.checkout(100);
// Pay using PayPal
cart.setPaymentStrategy(new PayPalPayment("user@example.com"));
cart.checkout(200);
}
}
This pattern is particularly useful in scenarios where we need to switch between different algorithms or behaviors dynamically, such as payment methods in an e-commerce application.
References: