Test Driven Development
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development approach where we write tests before writing the actual code.
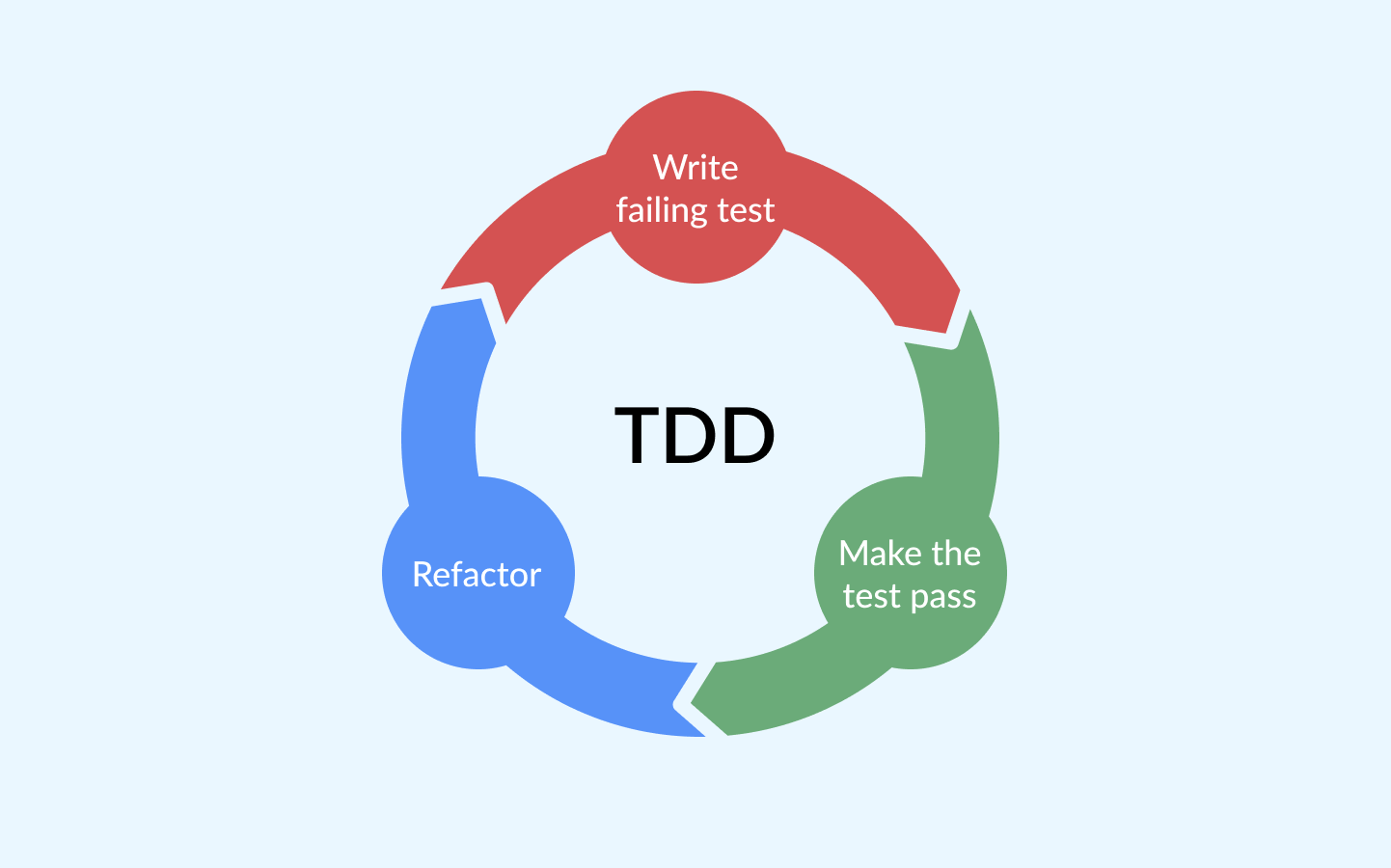
Here’s a brief overview of the process:
- Write a Test: Start by writing a test for a new feature or functionality. This test will initially fail because the feature hasn’t been implemented yet.
- Run the Test: Execute the test to confirm that it fails. This step ensures that the test is valid and that the feature is not already present.
- Write Code: Write the minimum amount of code necessary to make the test pass.
- Run the Test Again: Execute the test again to see if it passes with the new code.
- Refactor: Clean up the code while ensuring that the test still passes. This step improves code quality without changing its behavior.
- Repeat: Continue this cycle for each new feature or functionality.
The main benefits of TDD include:
- Improved Code Quality: By writing tests first, we ensure that our code meets the requirements and is less prone to bugs.
- Simplified Debugging: Since tests are written for small units of code, it’s easier to identify and fix issues.
- Better Design: TDD encourages developers to think about the design and requirements before writing code, leading to more modular and maintainable code.
Reference: